VPNs Questions
|
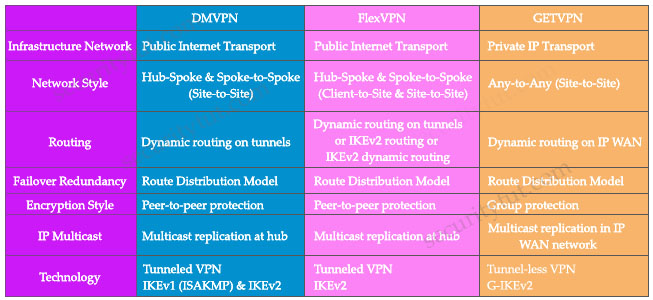
Quick summary DMVPN provides full meshes connectivity with simple configuration of hub and spoke. DMVPN forms IPsec tunnel over dynamically/statically addresses spokes. GETVPN (Group Encrypted Transport VPN) is a tunnel-less VPN technology meant for private networks like MPLS VPN or Private WAN where we use a single SA (Security Association) for all routers in a group. It is scalable for any-to-any connectivity and encryption. FlexVPN uses a new key management protocol – IKEv2 DMVPN, FlexVPN and GETVPN comparison:
|
Question 1
Explanation
The syntax of above command is:
crypto isakmp key enc-type-digit keystring {address peer-address [mask] | ipv6 ipv6-address/ ipv6-prefix | hostname hostname} [no-xauth]
The peer-address argument specifies the IP or IPv6 address of the remote peer.
Question 2
Explanation
Cisco‘s Group Encrypted Transport VPN (GETVPN) introduces the concept of a trusted group to eliminate point-to-point tunnels and their associated overlay routing. All group members (GMs) share a common security association (SA), also known as a group SA. This enables GMs to decrypt traffic that was encrypted by any other GM.
GETVPN provides instantaneous large-scale any-to-any IP connectivity using a group IPsec security paradigm.
Question 3
Explanation
Stateful failover for IP Security (IPsec) enables a router to continue processing and forwarding IPsec packets after a planned or unplanned outage occurs. Customers employ a backup (secondary) router that automatically takes over the tasks of the active (primary) router if the active router loses connectivity for any reason. This failover process is transparent to users and does not require adjustment or reconfiguration of any remote peer.
Stateful failover for IPsec requires that your network contains two identical routers that are available to be either the primary or secondary device. Both routers should be the same type of device, have the same CPU and memory, and have either no encryption accelerator or identical encryption accelerators.
Prerequisites for Stateful Failover for IPsec
Complete, Duplicate IPsec and IKE Configuration on the Active and Standby Devices
This document assumes that you have a complete IKE and IPsec configuration.
The IKE and IPsec configuration that is set up on the active device must be duplicated on the standby device. That is, the crypto configuration must be identical with respect to Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) policy, ISAKMP keys (preshared), IPsec profiles, IPsec transform sets, all crypto map sets that are used for stateful failover, all access control lists (ACLs) that are used in match address statements on crypto map sets, all AAA configurations used for crypto, client configuration groups, IP local pools used for crypto, and ISAKMP profiles.
Although the prerequisites only stated that “Both routers should be the same type of device” but in the “Restrictions for Stateful Failover for IPsec” section of the link above, it requires “Both the active and standby devices must run the identical version of the Cisco IOS software” so answer E is better than answer B.
Question 4
Explanation
FlexVPN is an IKEv2-based VPN technology that provides several benefits beyond traditional site-to-site VPN implementations. FlexVPN is a standards-based solution that can interoperate with non-Cisco IKEv2 implementations. Therefore FlexVPN can support a multivendor environment. All of the three VPN technologies support traffic between sites (site-to-site or spoke-to-spoke).
Question 5
Question 6
Question 7
Question 8
Explanation
DTLS is used for delay sensitive applications (voice and video) as its UDP based while TLS is TCP based. Therefore DTLS offers strongest throughput performance. The throughput of DTLS at the time of AnyConnect connection can be expected to have processing performance close to VPN throughput.
Question 9
Explanation
In its essence, FlexVPN is the same as DMVPN. Connections between devices are still point-to-point GRE tunnels, spoke-to-spoke connectivity is still achieved with NHRP redirect message, IOS routers even run the same NHRP code for both DMVPN and FlexVPN, which also means that both are Cisco’s proprietary technologies.
Reference: https://packetpushers.net/cisco-flexvpn-dmvpn-high-level-design/



Question 8 the correct should be D? pls help
@Anonymous: Yes, thanks for your detection, we have just updated Q.8.
Thanks for the confirmation @securitytut
please guys help me where can i get these questions …………………….
Please share questions for exam 300 – 730!! Please Please Please!!!
can i will appear in ccie lab after doing security paper 350-701
please share the study Material
Question 1 is wrong, please replace it:
“What is the result of running the crypto isakmp key ciscXXXXXXXX address 172.16.0.0 command?”
After running the commands on my router in my lab:
Router(config)#crypto isakmp key ciscXXXXXXXX address 172.16.0.0
Router(config)#do show crypto isakmp key
Keyring Hostname/Address Preshared Key
default 172.16.0.0 [255.255.0.0] ciscXXXXXXXX
As you see in the previous address the netmask is /16 (255.255.0.0)
@securitytut
Q7 answer should be C (C. FlexVPN uses IKEv2, DMVPN uses IKEv1 or IKEv2) you can check on cisco website for actual configuration of DMVPN using IKEV2
Please share questions for exam 300 – 730!! Please Please Please!!!
ahmedalobaidy1 at gmail dot com
Are we sure the answer to this question is still C?:
What is the result of running the crypto isakmp key ciscXXXXXXXX address 172.16.0.0 command?
A. authenticates the IKEv2 peers in the 172.16.0.0/16 range by using the key ciscXXXXXXXX
B. secures all the certificates in the IKE exchange by using the key ciscXXXXXXXX
C. authenticates the IP address of the 172.16.0.0/32 peer by using the key ciscXXXXXXXXcorrect
D. authenticates the IKEv1 peers in the 172.16.0.0/16 range by using the key ciscXXXXXXXX
Wouldn’t it default to the /16 subnet range if not specified?
@Corey
No. The correct answer is C. This command requires you to provide the unicast address of the VPN peer. a unicast address is /32
Hi All,
Rgding Q1.
Based on this cisco article it seems we need to specify the IP with mask. But in a case of mask is not define should we take what the cisco device take as default
Router(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco-10 address 172.16.0.12 255.240.0.0
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/sec_conn_vpnips/configuration/xe-16-9/sec-sec-for-vpns-w-ipsec-xe-16-9-book/sec-ipv6-ipv4-gre.html
Appreciate your feedback
Hi, lot of the questions have been removed it seems. Is it goes they won’t be in the exam any more? I am planning to take the exam tomorrow, before the syllabus changes. hope the questions are still valid.
So what is the correct answer on Q1?
The correct answer to Q1 is definitely B. The syntax of the command requires a Peer address which is a “/32”. Any other subnet mask would make the IP address a network address, making the command invalid.
Hi, I need to renew my CCNP RS. I work with ASA, FTD, ISE…Is SCOR a way to go, is it much harder or should I stick with the ENCOR?
thank you