Exfiltration Techniques
Question 1
Question 2
Explanation
DNS Tunneling is a method of cyber attack that encodes the data of other programs or protocols in DNS queries and responses. DNS tunneling often includes data payloads that can be added to an attacked DNS server and used to control a remote server and applications.
Question 3
Explanation
Domain name system (DNS) is the protocol that translates human-friendly URLs, such as securitytut.com, into IP addresses, such as 183.33.24.13. Because DNS messages are only used as the beginning of each communication and they are not intended for data transfer, many organizations do not monitor their DNS traffic for malicious activity. As a result, DNS-based attacks can be effective if launched against their networks. DNS tunneling is one such attack.
An example of DNS Tunneling is shown below:
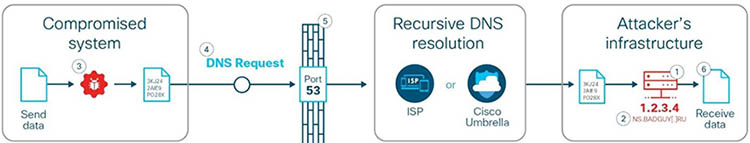
1. The attacker incorporates one of many open-source DNS tunneling kits into an authoritative DNS nameserver (NS) and malicious payload.
2. An IP address (e.g. 1.2.3.4) is allocated from the attacker’s infrastructure and a domain name (e.g. attackerdomain.com) is registered or reused. The registrar informs the top-level domain (.com) nameservers to refer requests for attackerdomain.com to ns.attackerdomain.com, which has a DNS record mapped to 1.2.3.4
3. The attacker compromises a system with the malicious payload. Once the desired data is obtained, the payload encodes the data as a series of 32 characters (0-9, A-Z) broken into short strings (3KJ242AIE9, P028X977W,…).
4. The payload initiates thousands of unique DNS record requests to the attacker’s domain with each string as a part of the domain name (e.g. 3KJ242AIE9.attackerdomain.com). Depending on the attacker’s patience and stealth, requests can be spaced out over days or months to avoid suspicious network activity.
5. The requests are forwarded to a recursive DNS resolver. During resolution, the requests are sent to the attacker’s authoritative DNS nameserver,
6. The tunneling kit parses the encoded strings and rebuilds the exfiltrated data.
Reference: https://learn-umbrella.cisco.com/i/775902-dns-tunneling/0
Question 4



Question 4 correct is C E
@Anonymous: Thanks for your detection, we have just updated Q.4.