Cloud Questions
|
Cloud Quick Summary Types of clouds There are 4 types of cloud: + Private Cloud: cloud that is dedicated solely to one organization. Advantages of Private Clouds are high security, Regulatory compliance, Flexibility to respond to changing needs. Drawbacks of private cloud are cost, mobile difficulty, Cloud services There are 3 main types of as-a-Service solutions: SaaS, PaaS and IaaS + SaaS (Software as a Service): SaaS uses the web to deliver applications that are managed by a third-party vendor and whose interface is accessed on the clients’ side. Most SaaS applications can be run directly from a web browser without any downloads or installations required, although some require plugins.
|
Question 1
Question 2
Question 3
Explanation
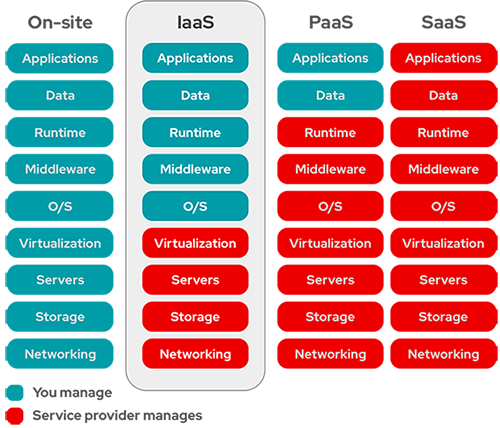
Only in On-site (on-premises) and IaaS we (tenant) manage O/S (Operating System).
Question 4
Explanation
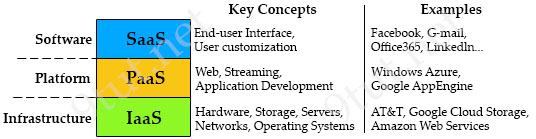
Cloud computing can be broken into the following three basic models:
+ Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS describes a cloud solution where you are renting infrastructure. You purchase virtual power to execute your software as needed. This is much like running a virtual server on your own equipment, except you are now running a virtual server on a virtual disk. This model is similar to a utility company model because you pay for what you use.
+ Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS provides everything except applications. Services provided by this model include all phases of the system development life cycle (SDLC) and can use application programming interfaces (APIs), website portals, or gateway software. These solutions tend to be proprietary, which can cause problems if the customer moves away from the provider’s platform.
+ Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS is designed to provide a complete packaged solution. The software is rented out to the user. The service is usually provided through some type of front end or web portal. While the end user is free to use the service from anywhere, the company pays a peruse fee.
Reference: CCNP and CCIE Security Core SCOR 350-701 Official Cert Guide
Question 5
Question 6
Question 7
Question 8
Question 9



q9 should be controls malicious cloud apps ?
In https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/security/cloudlock/index.html#~features states that:
Data security:
Cloudlock’s data loss prevention (DLP) technology continuously monitors cloud environments to detect and secure sensitive information. It provides countless out-of-the-box policies as well as highly tunable custom policies.
So, A is correct.
For question 3 explanation, I believe the screenshot is wrong. In SaaS model the service provider cannot be responsible for data.
See cert guide CCNP and CCIE Security Core SCOR – Omar Santos
I paid for a membership, is there a dump pdf still available or do I need to go through each question bank?