Security Products & Solutions
|
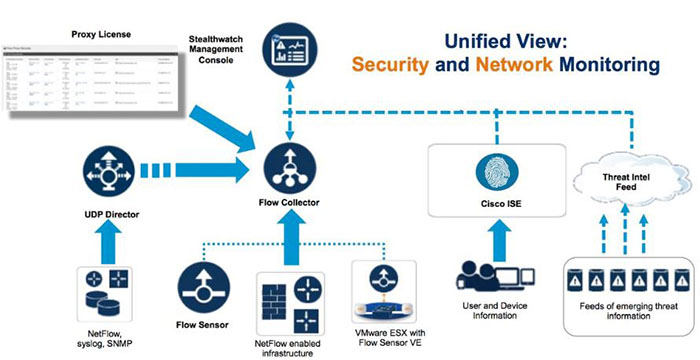
Quick summary + StealWatch: performs security analytics by collecting network flows via NetFlow Cisco SteathWatch Stealthwatch is the visibility and security analytics solution that collects and analyzes network data from the existing network infrastructure. Stealthwatch analyzes industry standard NetFlow data from Cisco and other vendors Routers, Switches, Firewalls, and other network devices to detect advanced and persistent security threats such as internally spreading malware, data leakage, botnet command and control traffic and network reconnaissance. The Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) solution supplements Stealthwatch NetFlowbased behavioral threat detection data with contextual information such as user identity, user authorization level, device-type, and posture. Together Stealthwatch and Cisco ISE present network security analysts with a view integrating NetFlow data and contextual information enabling the security analyst to detect and discern the potential severity of threats in a timely, efficient, and cost-effective manner. Stealthwatch components include:
Stealthwatch offers different deployment models: Cisco Stealthwatch Cloud: Available as an SaaS product offer to provide visibility and threat detection within public cloud infrastructures such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Cisco Cognitive Threat Analytics helps you quickly detect and respond to sophisticated, clandestine attacks that are already under way or are attempting to establish a presence within your environment. The solution automatically identifies and investigates suspicious or malicious web-based traffic. It identifies both potential and confirmed threats, allowing you to quickly remediate the infection and reduce the scope and damage of an attack, whether it’s a known threat campaign that has spread across multiple organizations or a unique threat you’ve never seen before.
|
Question 1
Explanation
Cisco Stealthwatch Cloud: Available as an SaaS product offer to provide visibility and threat detection within public cloud infrastructures such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Question 2
Explanation
Cisco Cognitive Threat Analytics helps you quickly detect and respond to sophisticated, clandestine attacks that are already under way or are attempting to establish a presence within your environment. The solution automatically identifies and investigates suspicious or malicious web-based traffic. It identifies both potential and confirmed threats, allowing you to quickly remediate the infection and reduce the scope and damage of an attack, whether it’s a known threat campaign that has spread across multiple organizations or a unique threat you’ve never seen before.
Detection and analytics features provided in Cognitive Threat Analytics are shown below:
+ Data exfiltration: Cognitive Threat Analytics uses statistical modeling of an organization’s network to identify anomalous web traffic and pinpoint the exfiltration of sensitive data. It recognizes data exfiltration even in HTTPS-encoded traffic, without any need for you to decrypt transferred content
+ Command-and-control (C2) communication: Cognitive Threat Analytics combines a wide range of data, ranging from statistics collected on an Internet-wide level to host-specific local anomaly scores. Combining these indicators inside the statistical detection algorithms allows us to distinguish C2 communication from benign traffic and from other malicious activities. Cognitive Threat Analytics recognizes C2 even in HTTPS-encoded or anonymous traffic, including Tor, without any need to decrypt transferred content, detecting a broad range of threats
…
Question 3
Explanation
The traditional use of the pull model, where the client requests data from the network does not scale when what you want is near real-time data. Moreover, in some use cases, there is the need to be notified only when some data changes, like interfaces status, protocol neighbors change etc.
Model-Driven Telemetry is a new approach for network monitoring in which data is streamed from network devices continuously using a push model and provides near real-time access to operational statistics. Applications can subscribe to specific data items they need, by using standard-based YANG data models over NETCONF-YANG. Cisco IOS XE streaming telemetry allows to push data off of the device to an external collector at a much higher frequency, more efficiently, as well as data on-change streaming.
Reference: https://developer.cisco.com/docs/ios-xe/#!streaming-telemetry-quick-start-guide
Question 4
Explanation
Telemetry – Information and/or data that provides awareness and visibility into what is occurring on the network at any given time from networking devices, appliances, applications or servers in which the core function of the device is not to generate security alerts designed to detect unwanted or malicious activity from computer networks.
Question 5
Explanation
Cisco Threat Intelligence Director (CTID) can be integrated with existing Threat Intelligence Platforms (ThreatQ, AlienVault, Infoblox etc) deployed by your organization to ingest threat intelligence automatically.
Note: ThreatQ, AlienVault, Infoblox etc are external Threat Intelligence Platforms
Threat Intelligence Director – Feature introduced: Lets you use threat intelligence from external sources to identify and process threats.
Question 6
Explanation
The Cisco Application Visibility and Control (AVC) solution leverages multiple technologies to recognize, analyze, and control over 1000 applications, including voice and video, email, file sharing, gaming, peer-to-peer (P2P), and cloud-based applications. AVC combines several Cisco IOS/IOS XE components, as well as communicating with external tools, to integrate the following functions into a powerful solution…
Question 7
Explanation
Cisco DNA Center has four general sections aligned to IT workflows:
Design: Design your network for consistent configurations by device and by site. Physical maps and logical topologies help provide quick visual reference. The direct import feature brings in existing maps, images, and topologies directly from Cisco Prime Infrastructure and the Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module (APIC-EM), making upgrades easy and quick. Device configurations by site can be consolidated in a “golden image” that can be used to automatically provision new network devices. These new devices can either be pre-staged by associating the device details and mapping to a site. Or they can be claimed upon connection and mapped to the site.
Policy: Translate business intent into network policies and apply those policies, such as access control, traffic routing, and quality of service, consistently over the entire wired and wireless infrastructure. Policy-based access control and network segmentation is a critical function of the Cisco Software-Defined Access (SD-Access) solution built from Cisco DNA Center and Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE). Cisco AI Network Analytics and Cisco Group-Based Policy Analytics running in the Cisco DNA Center identify endpoints, group similar endpoints, and determine group communication behavior. Cisco DNA Center then facilitates creating policies that determine the form of communication allowed between and within members of each group. ISE then activates the underlying infrastructure and segments the network creating a virtual overlay to follow these policies consistently. Such segmenting implements zero-trust security in the workplace, reduces risk, contains threats, and helps verify regulatory compliance by giving endpoints just the right level of access they need.
Provision: Once you have created policies in Cisco DNA Center, provisioning is a simple drag-and-drop task. The profiles (called scalable group tags or “SGTs”) in the Cisco DNA Center inventory list are assigned a policy, and this policy will always follow the identity. The process is completely automated and zero-touch. New devices added to the network are assigned to an SGT based on identity—greatly facilitating remote office setups.
Assurance: Cisco DNA Assurance, using AI/ML, enables every point on the network to become a sensor, sending continuous streaming telemetry on application performance and user connectivity in real time. The clean and simple dashboard shows detailed network health and flags issues. Then, guided remediation automates resolution to keep your network performing at its optimal with less mundane troubleshooting work. The outcome is a consistent experience and proactive optimization of your network, with less time spent on troubleshooting tasks.
Question 8
Question 9
Explanation
With Cisco pxGrid (Platform Exchange Grid), your multiple security products can now share data and work together. This open, scalable, and IETF standards-driven platform helps you automate security to get answers and contain threats faster.
Question 10
Question 11
Explanation
Cisco Context Directory Agent (CDA) is a mechanism that maps IP Addresses to usernames in order to allow security gateways to understand which user is using which IP Address in the network, so those security gateways can now make decisions based on those users (or the groups to which the users belong to).
CDA runs on a Cisco Linux machine; monitors in real time a collection of Active Directory domain controller (DC) machines for authentication-related events that generally indicate user logins; learns, analyzes, and caches mappings of IP Addresses and user identities in its database; and makes the latest mappings available to its consumer devices.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/ibf/cda_10/Install_Config_guide/cda10/cda_oveviw.html




Question 4 I think is D!
Q4: why prime? should it not be Telemetry?
What can be integrated with Cisco Threat Intelligence Director to provide information about security threats, which allows the SOC to proactively automate responses to those threats?
A. Cisco Umbrella
B. External Threat Feeds
C. Cisco Threat Grid
D. Cisco Stealthwatch
I think it’s B the correct answer.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/storage-networking/security/214859-configure-and-troubleshoot-cisco-threat.html
“on the FMC you have to configure sources from where you would like to download threat intelligence information”, so I think B and not C..
Q5 .> why not B??
Q5 is B
@Admin
Hi Admin,
I agree with bobo77, as per the given Cisco document,
Cisco Threat Intelligence Director (TID) is a system that operationalizes threat intelligence information. The system consumes and normalizes heterogeneous third-party cyber threat intelligence, publishes the intelligence to detection technologies and correlates the observations from the detection technologies.
Even the link given in the explanation section mentioned third party Threat Intelligence Platforms (ThreatQ, AlienVault, Infoblox).
Please review and correct if necessary.
@bobo77, @Ash: Yes, thanks for your detection, B is the better answer and we updated Q.5.
How to loginto premium acct ?
Q5 Correct Aswer is B
Question 5
What can be integrated with Cisco Threat Intelligence Director to provide information about security threats, which allows the SOC to proactively automate responses to those threats?
A. Cisco Umbrella
B. External Threat Feeds
C. Cisco Threat Grid
D. Cisco Stealthwatch
C i correct
proof: page 33 of https://www.ciscolive.com/c/dam/r/ciscolive/apjc/docs/2018/pdf/DEVNET-2164.pdf
@pong: We reviewed Q5 again but still believed B is the best choice.
Threat Intelligence Director – Feature introduced: Lets you use threat intelligence from external sources to identify and process threats.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/firepower/623/configuration/guide/fpmc-config-guide-v623/cisco_threat_intelligence_director__tid_.html
Just a thought. Maybe it would be more meaningful to put this section on top of the menu, above security concepts